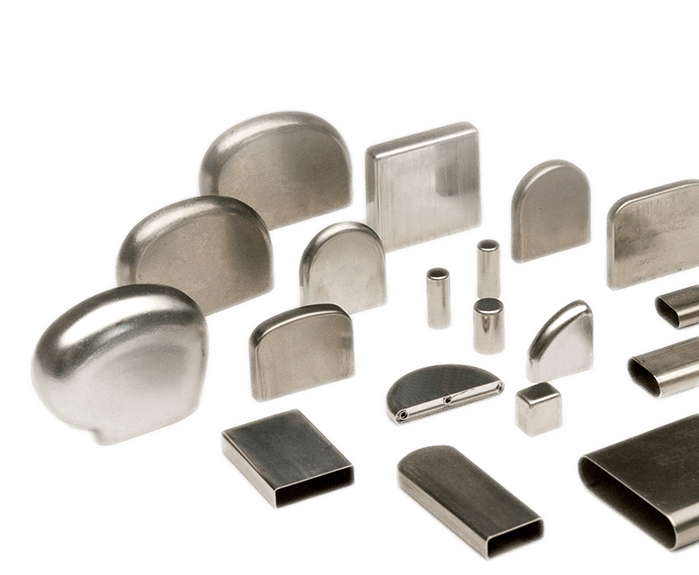
Over 15,000 Standard Products
Our catalog contains 15,000+ round, square, and rectangular cases and covers, and relay cases with little or no tooling costs and fast lead times! We also offer the option to add customized finishes or modifications to suit your needs.
To view our catalog, select the option that fits you below.

OUR METAL DRAWING AND METAL STAMPING SERVICES
Hudson Technologies' core capabilities in deep drawn stamping are based on our expertise with a variety of high-performance metals, such as stainless steel and titanium, along with aluminum, cold rolled steel, brass, copper, HyMu80 (other shielding alloys available), nickel, and cupro nickel. From customized metal enclosures, cases and covers to metal diaphragms or semiconductor components, our team can meet clients’ specific application needs and specifications — no matter how unusual or complex. Our technical support team works closely with customers from start to finish.
Industries
Hudson Technologies has been providing industry-leading custom metal stamping and deep drawn stamping services for a range of different industries.
The aerospace industry supplies parts and products to five key market sectors: commercial airlines, general aviation, military aircraft, missiles, and space research. As the components supplied often find application in critical operations where failure is not an option, it is essential they feature high precision, accuracy, durability, and reliability to ensure they function as intended.
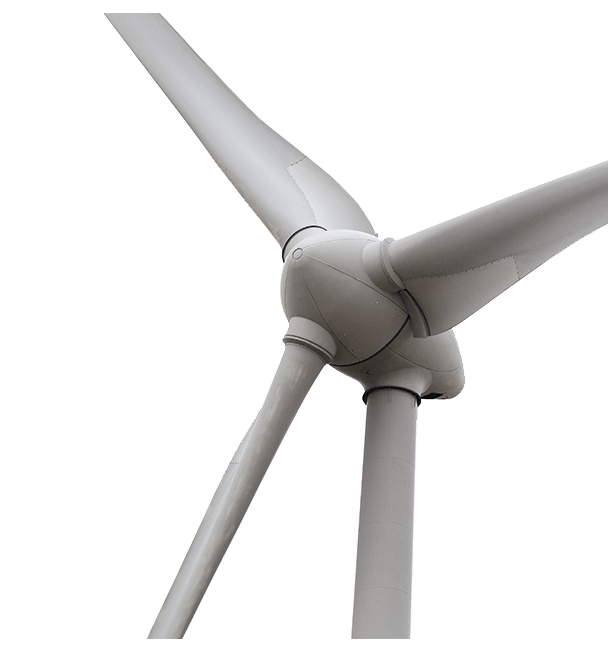
Hudson Technologies produces deep drawn metal battery enclosures for a variety of industries, including energy storage. In recent years, we’ve worked to provide innovative solutions to any company working to store energy from intermittent or renewable sources such as wind and solar power.
Manufacturing implantable medical devices requires products to achieve a high degree of precision and quality. Hudson Technologies uses state-of-the-art deep-draw manufacturing techniques to create parts that satisfy the three main requirements of building medical equipment:
- Clean medical components
- Cutting-edge, precision equipment
Parts and equipment manufactured for use by the U.S. military and Department of Defense (DOD) must comply with stringent military specifications (Mil-Spec). Mil-Spec includes tight tolerances for dimensions of parts and the ability of equipment to withstand extreme ambient conditions in storage and in operation.
The world currently runs on fossil fuels. As the global population increases and production demands rise, the need for oil and natural gas will continue to grow as well. To meet these needs, riskier drilling processes will be required. It’s important that oil and gas stakeholders use quality equipment to mitigate the environmental and safety risks of these methods.
Semiconductor and semiconductor wafer fabrication requires an extremely high degree of precision and adherence to strict industry requirements. As such, it’s important that parts used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment exhibit exceptional quality and performance.



Serving Industries Worldwide Since 1940
HUDSON TECHNOLOGIES CATALOG
Our catalog has over 15,000 standard shapes & sizes of metal cases, covers, enclosures and diaphragms to meet many application specifications with little to no tooling charges.
Facility and Equipment
Hudson Technologies houses machines built to meet your specific metal drawing or metal stamping needs.
About Us
Hudson Technologies is a leading U.S. manufacturer of deep drawn metal enclosures, or cases, and stampings, including metal diaphragms. Design engineers turn to Hudson Technologies for custom enclosures and metal diaphragms for all their equipment needs, whether they require a prototype or high-volume production. Our green manufacturing services include a full range of customization options, and our team is committed to close collaboration throughout every step of the process - from design to final production. In this way, we’re fully dedicated to forming partners through collaboration.